Definition:
The digital counterpart of an entity in the analog world, such as a physical device, or a service. Digital twins provide a virtual representation that enables the addition of functionality, such as information repositories and communication channels for interaction.
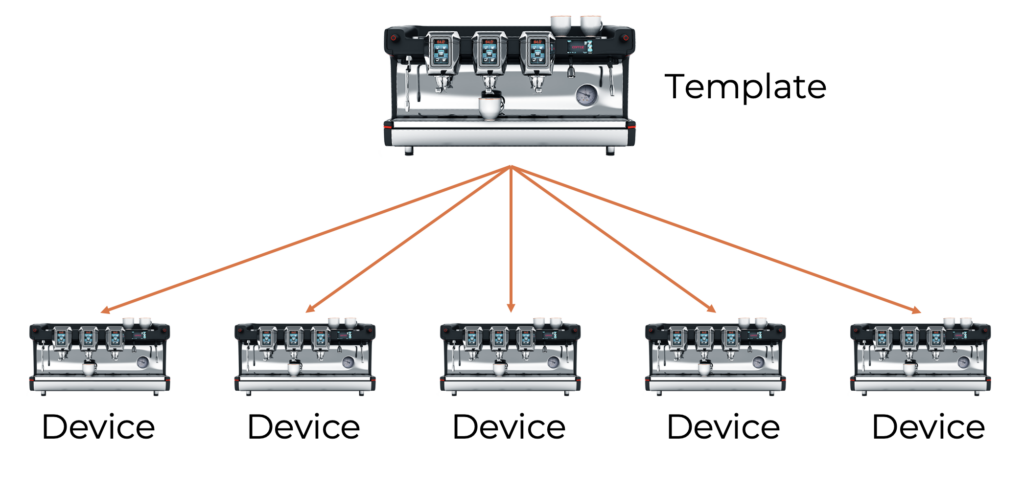
Structure and Synchronization:
- Every device within the platform is based on a template, from which it inherits the majority of its content through permanent synchronization.
- Note: Synchronization can be customized or stopped by:
- Detaching specific submodules/modules in the device settings.
- Overwriting inherited template content with device-specific information.
- Note: Synchronization can be customized or stopped by:
Stored Information:
- Template-Specific Information:
- Includes general details such as device descriptions, manuals, and standard instructions.
- Device-Specific Information:
- Contains unique details such as:
- Assigned customer information.
- Service history, including the digital service record, which tracks service cases over time.
- Contains unique details such as:
Key Benefits:
- Centralized Repository: Serves as a single source for device-specific data that is easily accessible.
- Advanced Functionalities: Enables remote diagnostics, updates, and support for devices.
- Traceability: Tracks device-specific interactions and service records, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
